
1 Wind Turbine Design. Download Scientific Diagram
September 21, 2023 Wind Energy Technologies Office Modeling the Future of Wind Energy Before computers and simulation software existed (i.e., until the mid-1980s), wind turbine manufacturers had to design and build prototypes of wind turbines in order to test and evaluate them, which was costly and time-consuming.

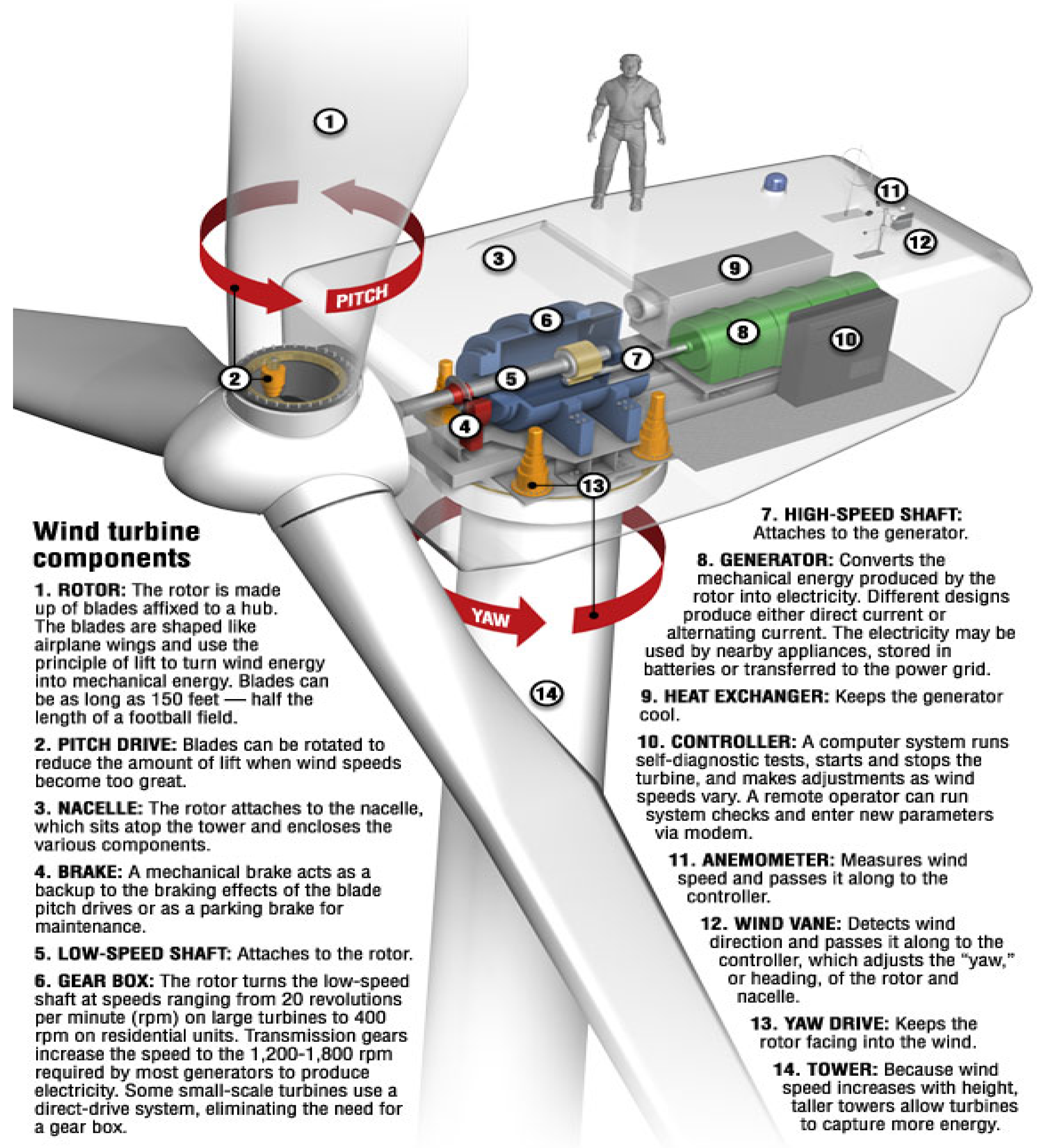
Main components of a horizontal axis wind turbine Download Scientific Diagram
Hence, a turbine spinning in the wind may seem simple, but designing and measuring blades of a wind turbine, using a sequence of changing cross-sectional shapes, requires a lot of sophisticated geometry. I'm part of a team studying abstractions of geometric methods to design better wind turbines with mathematics.

38 High Def Wind Turbine Pictures From Around the World
Accurate prediction of long‐term 'characteristic' loads associated with an ultimate limit state for design of a 5‐MW bottom‐supported offshore wind turbine is the focus of this study. Specifically, we focus on predicting the long‐term fore-aft tower bending moment at the mudline and the out‐of‐plane bending moment at the blade.
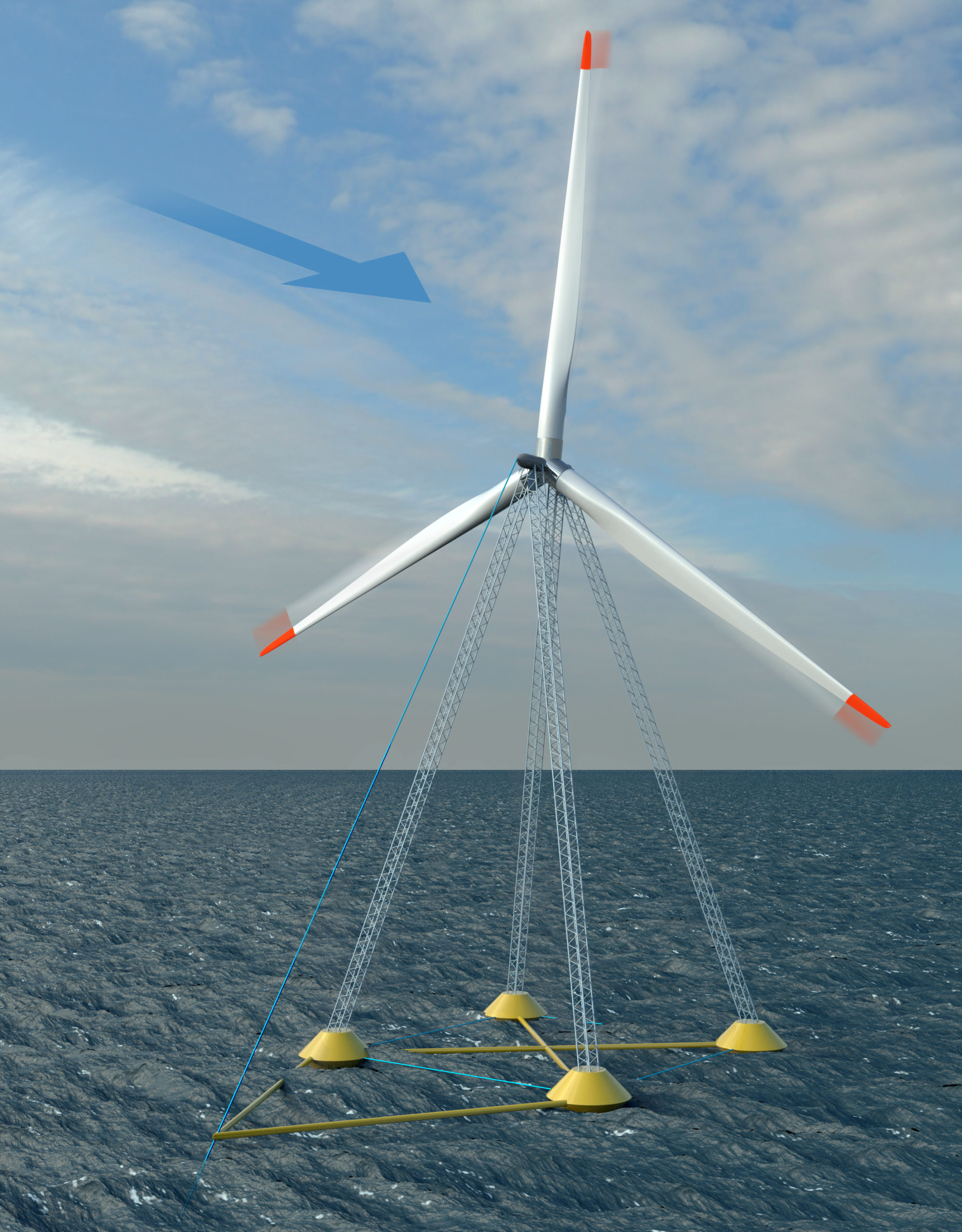
Myers Awarded MassCEC Grant for Innovative Floating Wind Turbine Northeastern University
Wind turbines in cold and humid regions face significant icing challenges. Heating is considered an efficient strategy to prevent ice accretion over the turbine's blade surface. An ice protection system is required to minimize freezing of the runback water at the back of the blade and the melting state of the ice on the blade; the law of re-freezing of the runback water is necessary for the.

GEDAYC Wind Turbine New Concept Create the Future Design Contest
Renewable energy portal Category v t e Wind power is the use of wind energy to generate useful work. Historically, wind power was used by sails, windmills and windpumps, but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. This article deals only with wind power for electricity generation.

NablaWave Srl Horizontalaxis wind turbine (HAWT)
As the wind business booms — not only in Texas but across the country and worldwide — engineers at The University of Texas at Dallas are driving innovation in wind-turbine design and efficiency, propelled by new research facilities and a state-of-the-art building that provide opportunities for students to learn and for industry partners to boost their bottom lines.
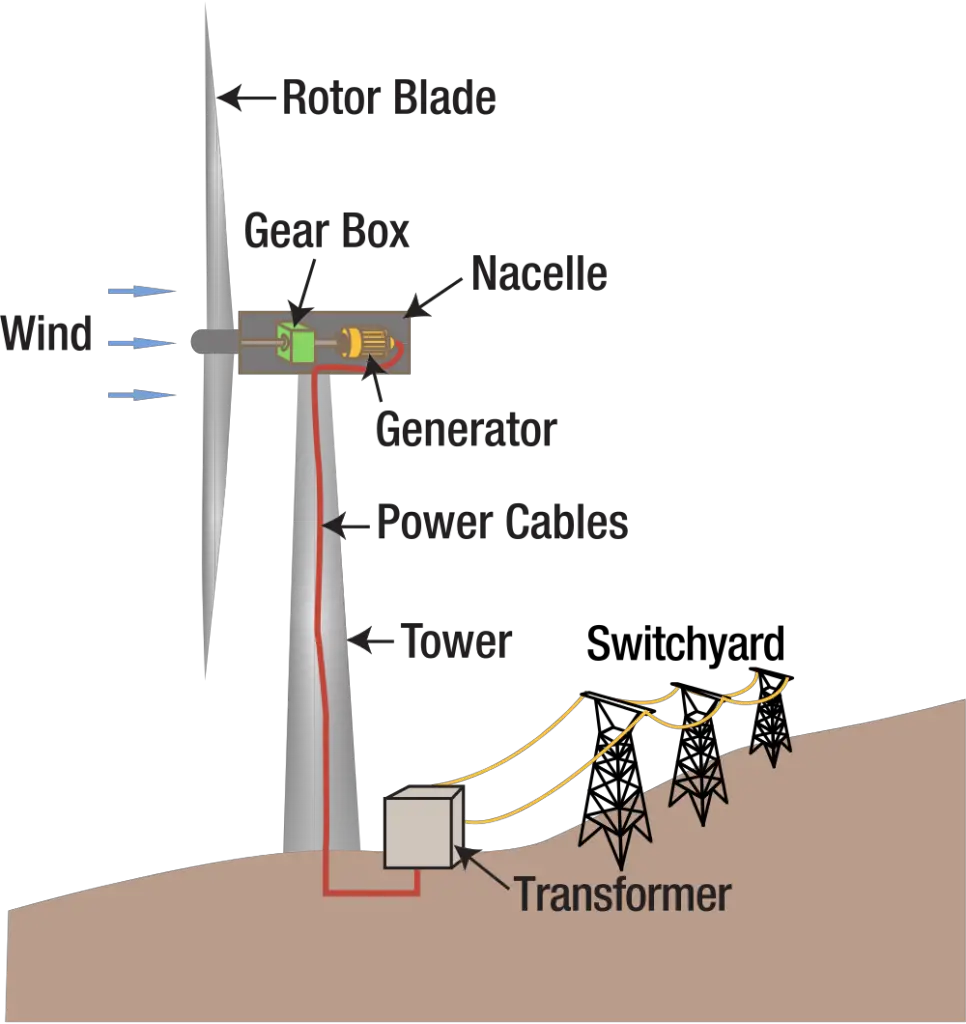
How Wind Power Plant Works? Complete Explanation Mechanical Booster
Technology Overview Beyond the Science and Technology What's underway @ MIT Wind Power in History. Brief History - Early Systems Harvesting wind power isn't exactly a new idea - sailing ships, wind-mills, wind-pumps 1st Wind Energy Systems Ancient Civilization in the Near East / Persia

Types of Wind Turbines Horizontal Axis and Vertical Axis Wind Turbines Mechanical Booster
Wind turbine design is the process of defining the form and configuration of a wind turbine to extract energy from the wind. [1] An installation consists of the systems needed to capture the wind's energy, point the turbine into the wind, convert mechanical rotation into electrical power, and other systems to start, stop, and control the turbine.
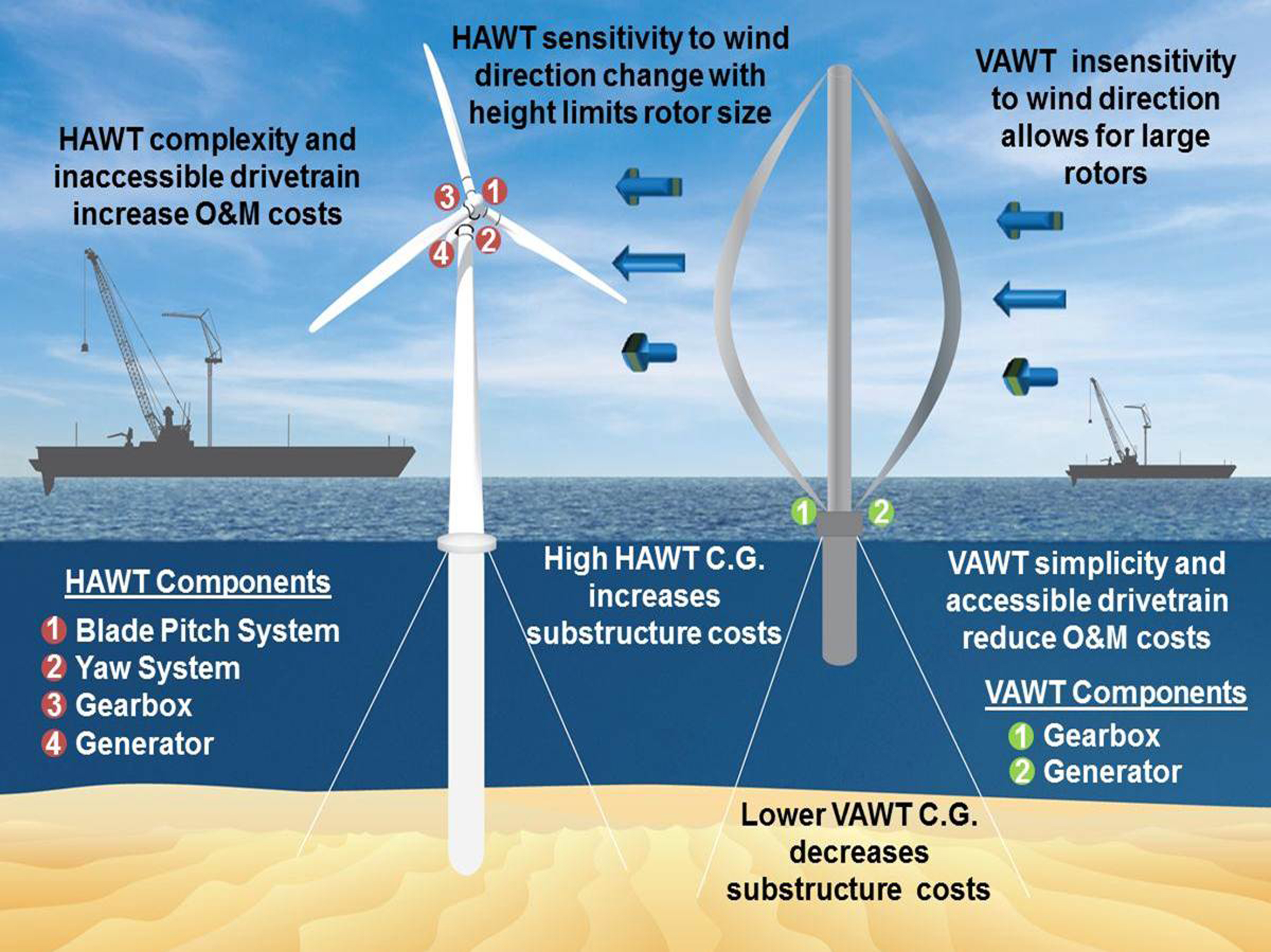
Sandia National Laboratories News Releases Offshore use of verticalaxis wind turbines gets
The Big Adaptive Rotor project works to design and enable the next generation of land-based wind turbines. 2020's most notable wind energy research and development accomplishments. The 2019 report presenting opportunities, challenges, and potential associated with increasing wind turbine tower heights.
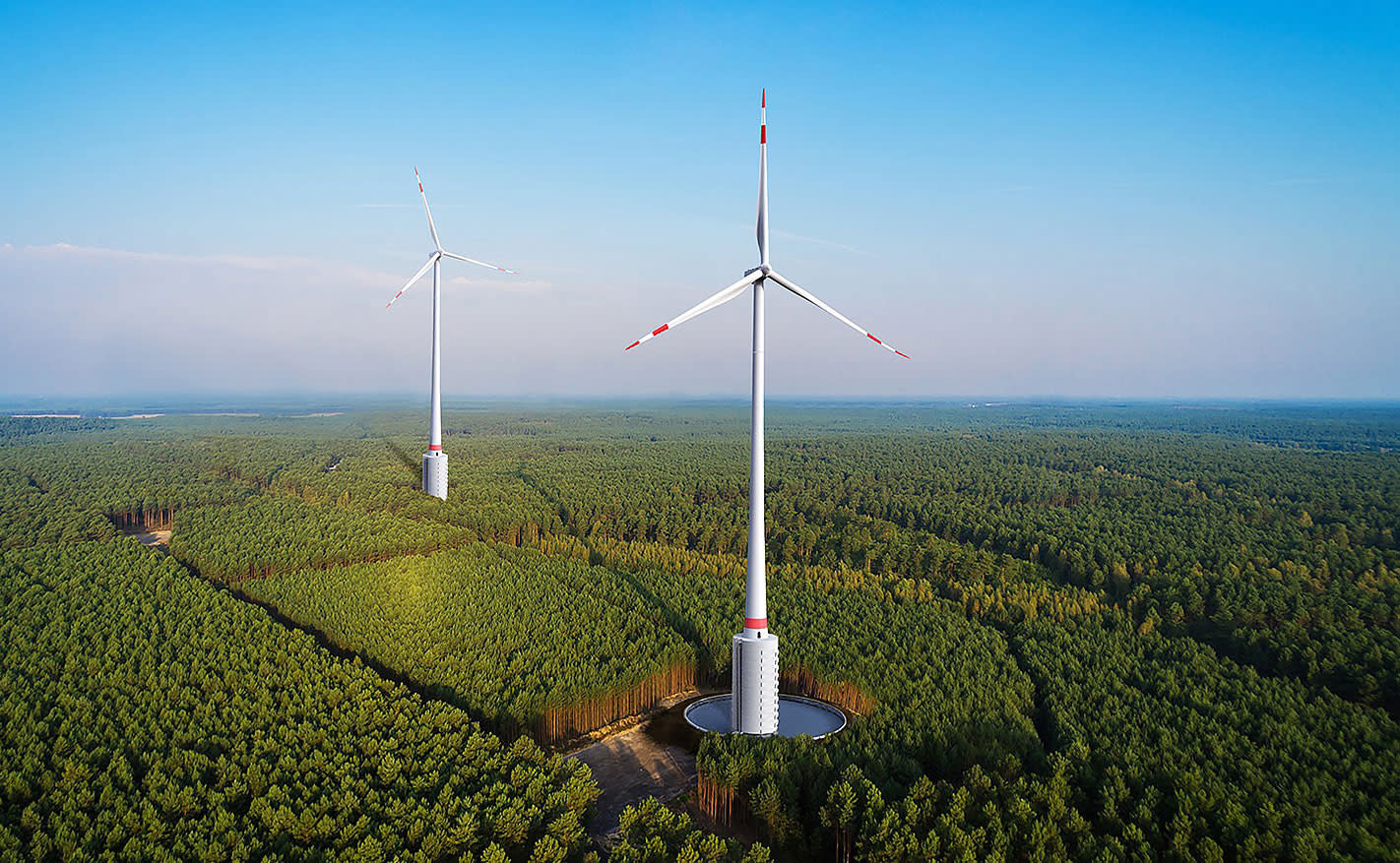

Six innovative wind turbine designs
Wind turbine design and technology has been developed over several decades. The main driving factor for wind energy is the cost of energy, which is the motivation for more efficient and larger turbines.
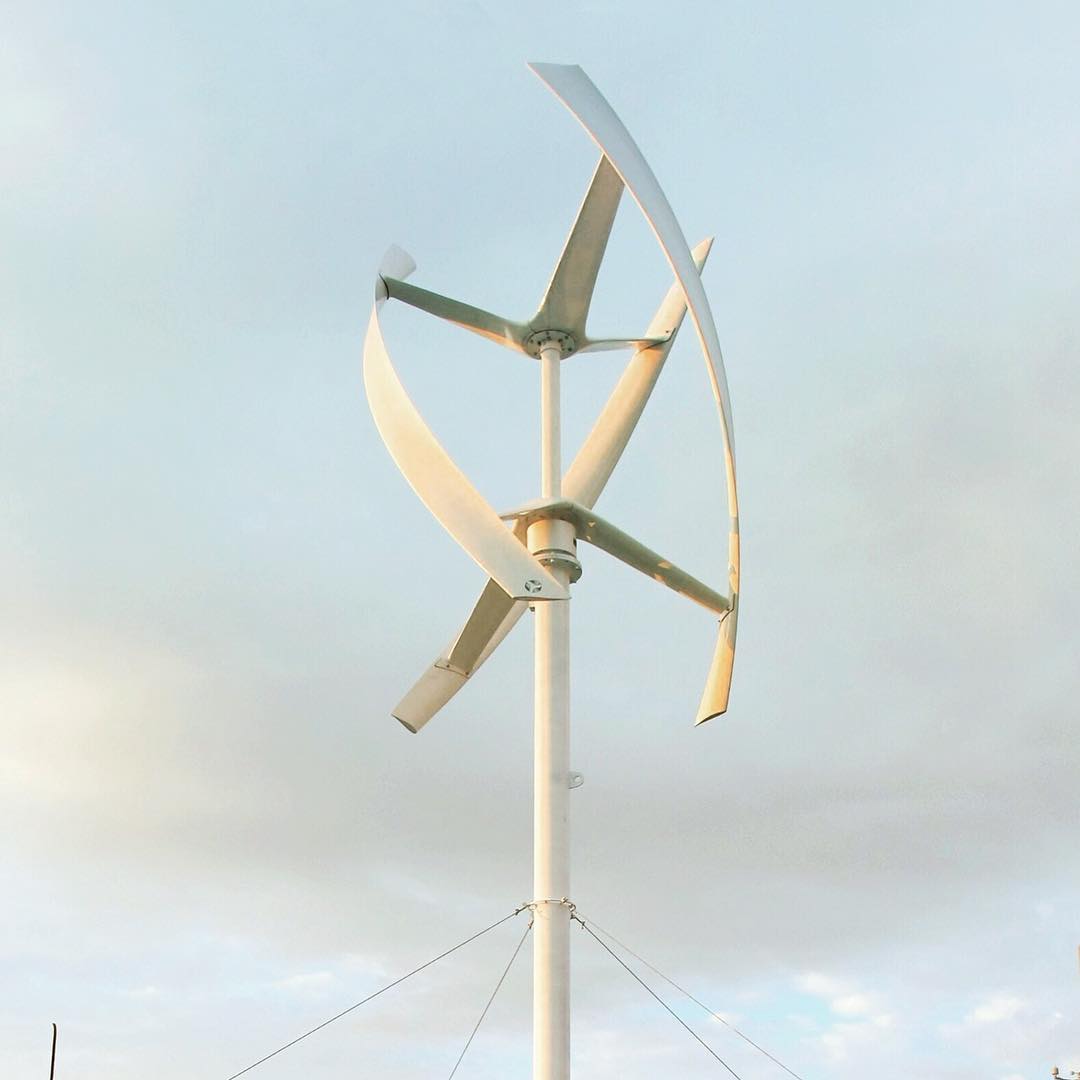

How to Choose Vertical Wind Turbines?
Dec. 27, 2023, 9:50 AM ET (AP) The year in clean energy: Wind, solar and batteries grow despite economic challenges. wind turbine, apparatus used to convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity. Wind turbines come in several sizes, with small-scale models used for providing electricity to rural homes or cabins and community -scale models.
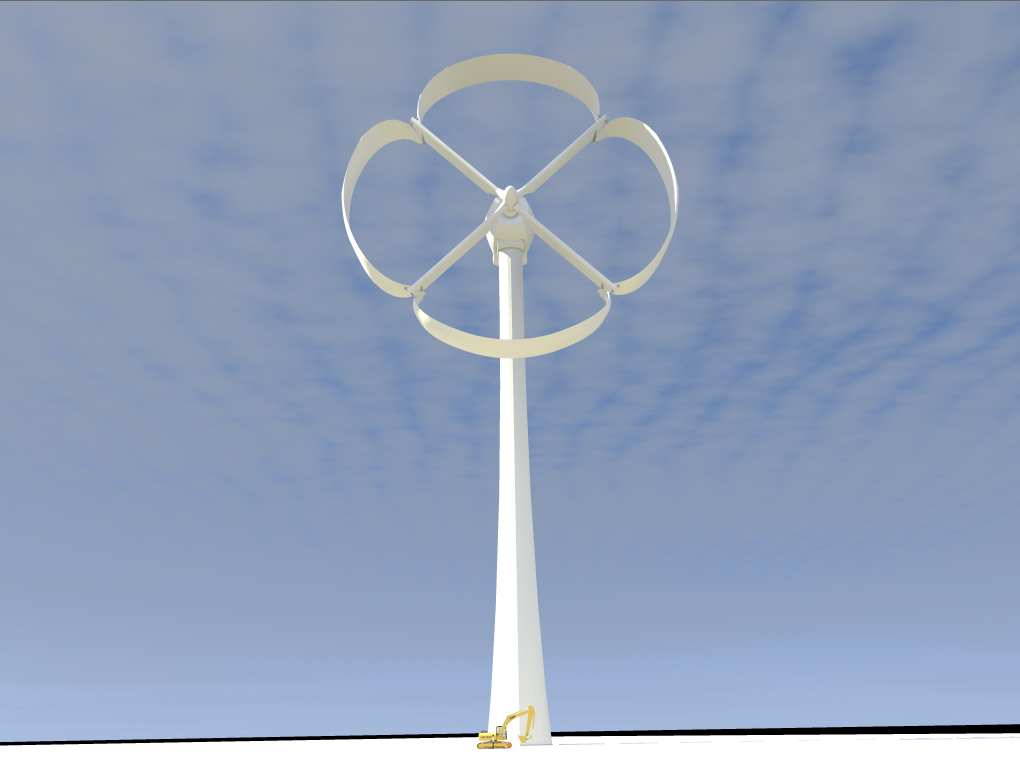

GEDAYC Wind Turbine 300 More Efficient Create the Future Design Contest
Wind power plants teaches the physical foundations of usage of Wind Power. It includes the areas like Construction of Wind Power Plants, Design, Development of Production Series, Control, and discusses the dynamic forces acting on the systems as well as the power conversion and its connection to the distribution system.
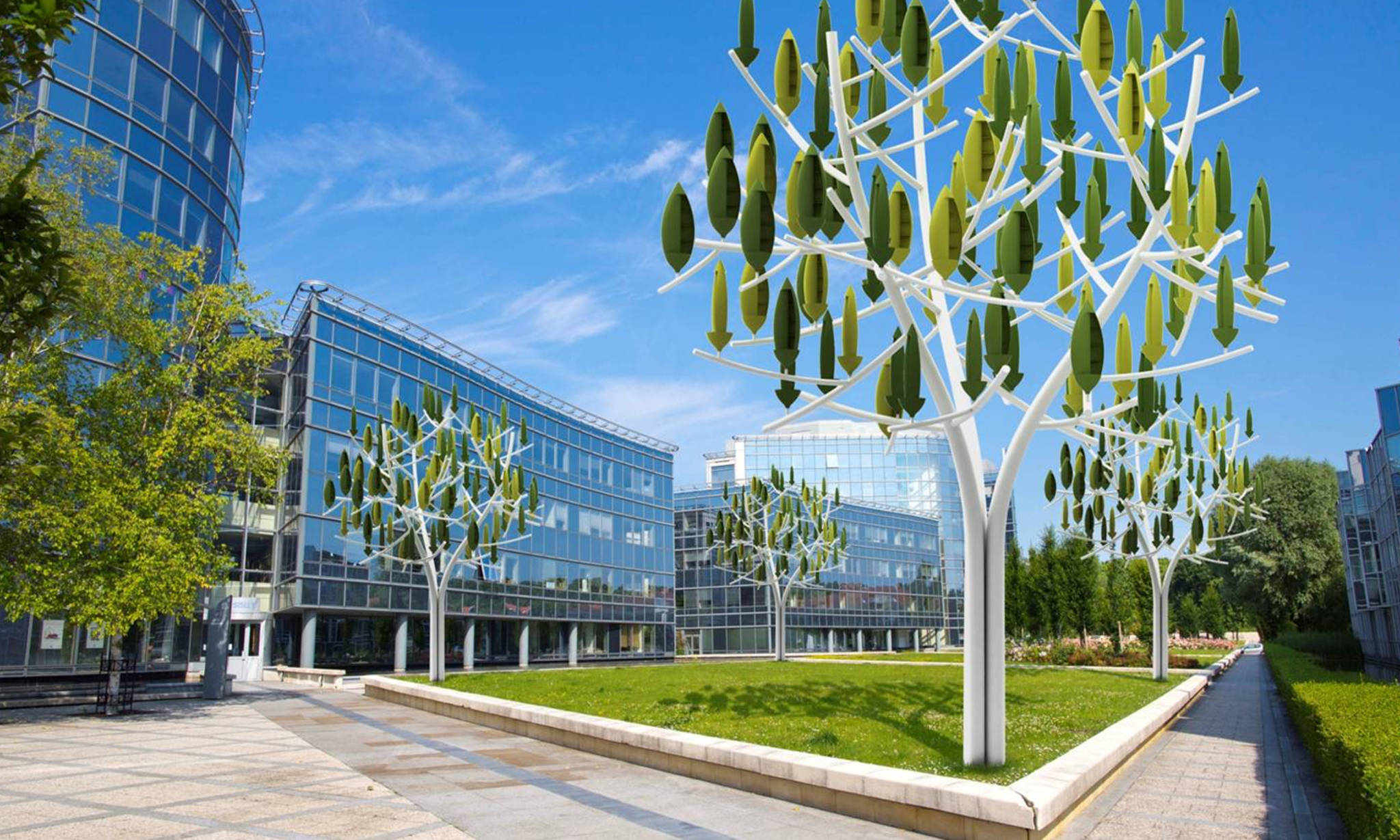

Power Grows on Trees Wind Energy via Leafy Green Turbines Urbanist
Modern turbine design is a testament to the unlimited creativity and ingenuity of today's engineers, but a few of these designs may leave you asking: How exactly is that supposed to work?.
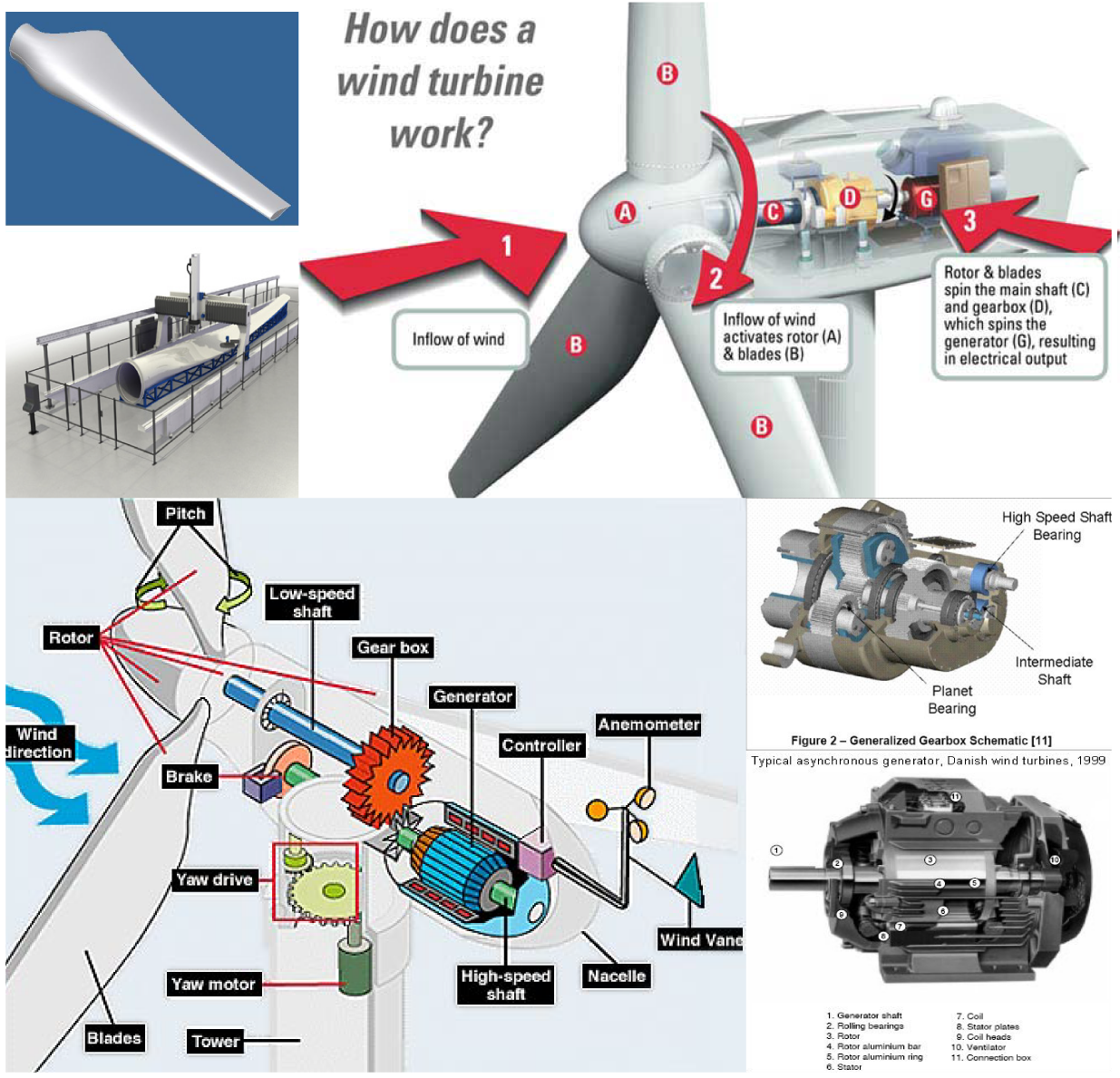
A Fundamental Introduction To How Wind Turbines Work How To Make Turbine & Go Green With It
Wind is one of the commonly used energy sources in energy harvesting, just like solar, hydro, thermo, and kinetic energy. It can generate electricity through traditional wind turbines or combine with smart materials such as piezoelectric materials for small-scale energy harvesting. 8 Because it is very suitable for the above-mentioned wireless sensor network and other similar systems, more and.

diy vertical axis wind turbine design Jaymie Kinsey
The global capacity for generating power from wind energy has grown continuously since 2001, reaching 591 GW in 2018 (9-percent growth compared to 2017), according to the Global Wind Energy Council [1].. In terms of technology, turbine design focuses on optimizing power output by focusing on two key parameters: blade length and average wind.
Energies Free FullText Wind Turbine Blade Design
Optimization of energy production Once the wind farm constraints are defined, the layout of the wind farm can be optimized - also called wind farm 'micro-siting'. For most projects, the economics are substantially more sensitive to changes in energy production than infrastructure costs.